
Hypermobility Artofit
poor co-ordination. some people find it difficult to sense the position of a joint without being able to see it, also known as proprioception. joint dislocations or partial dislocations. regular soft tissue injuries - such as sprains and sports injuries. easy bruising. stomach pain. bladder and bowel problems. dizziness.

4 ways to manage Hypermobility syndrome East Cornwall Osteopathy
Background: Joint hypermobility syndrome (JHS) is a heritable connective tissue disorder characterised by excessive range of movement at multiple joints accompanied by pain. Exercise is the mainstay of management yet its effectiveness is unclear. Objectives: To establish the effectiveness of therapeutic exercise for JHS. Design: Systematic literature review.

Too Flexible? Try These Exercises for Improving Hypermobility YouTube
The purpose of this review is to provide clinicians the rationale for the update in nomenclature, understand the musculoskeletal and extra-articular manifestations of the subtypes of HSDs, considerations when making the diagnosis, and treatment. Keywords: joint hypermobility, generalized joint hypermobility, joint hypermobility syndrome, benign.
Physical therapy for joint pain caused by hypermobility Capital Area
However, for some people, hypermobility causes joint pain, joint and ligament injuries, tiredness (fatigue), bowel issues and other symptoms. Joint hypermobility syndrome is most common in children and young people. It affects people assigned female at birth (AFAB) and people of Asian and Afro-Caribbean descent more often.
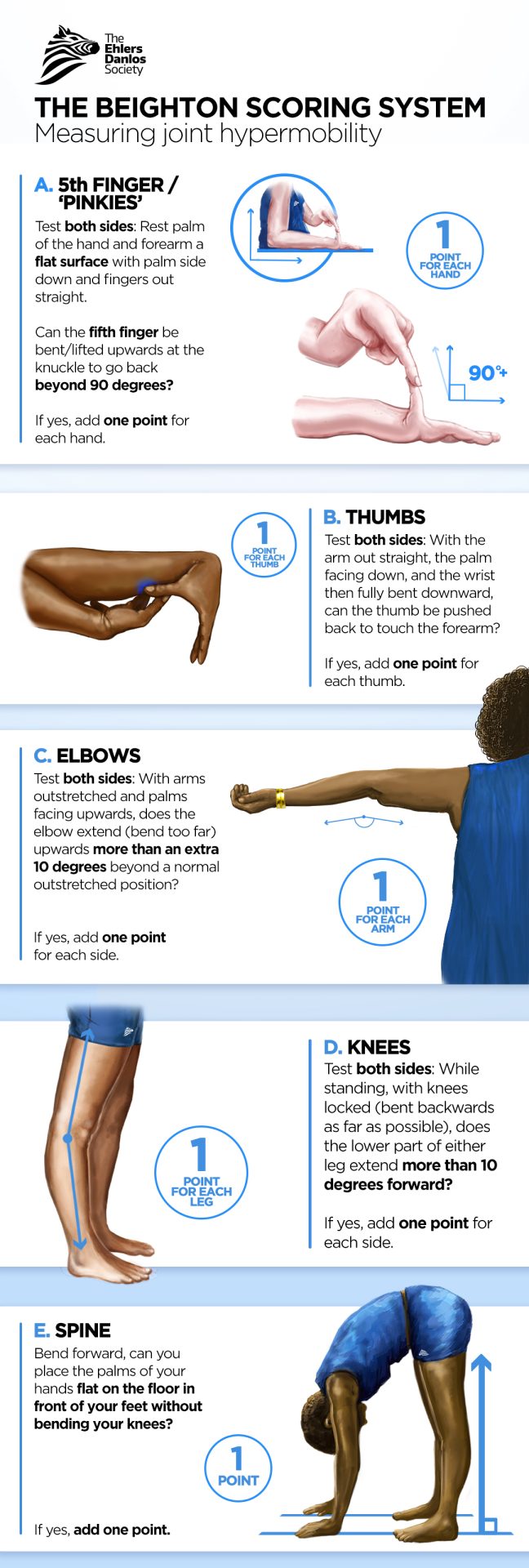
Assessing Joint Hypermobility The Ehlers Danlos Society
Joint hypermobility syndrome. Many people with hypermobile joints don't have any problems, and some people - such as ballet dancers, gymnasts and musicians - may actually benefit from the increased flexibility.. People with JHS often benefit from a combination of controlled exercise and physiotherapy, as well as additional help to.

Best exercise for Hypermobility http//www.physiofitcambridge.co.uk
Joint hypermobility without pain occurs when children have stretchy or flexible joints, but without exercise-related pain. This is an advantage to some children, and tends to be associated with being good at sport. HSDs are the diagnosis where the main or only symptoms are exercise-related pain, together with joint hypermobility.

EDSFitTip Practicing Yoga Safely with Joint Hypermobility (Clip 3
structures becomes deficient, joint hypermobility results. Joint hypermobility can be technically defined as excessive motion in the normal plane of a joint.3 It can be limited to one or a few joints, or be as widespread as to affect the majority of all joints in the body. The term "generalized joint hypermobility" (GJH) is used to describe.

3 Hypermobility Exercises YouTube
Symptoms of joint hypermobility syndrome. You or your child may have joint hypermobility syndrome if you: often get tired, even after rest. keep getting pain and stiffness in your joints or muscles. keep getting sprains and strains. keep dislocating your joints (they "pop out") have poor balance or co-ordination. have thin, stretchy skin.

Hyper Mobility Syndrome Children Conditions Paediatric What We
A 2017 article in the Journal of Education, Health and Sport recommended stabilization exercises for people with hypermobility. These movements rely on closed kinetic chain exercises, which increase muscle awareness and work many joints. Examples include power squats and rowing.

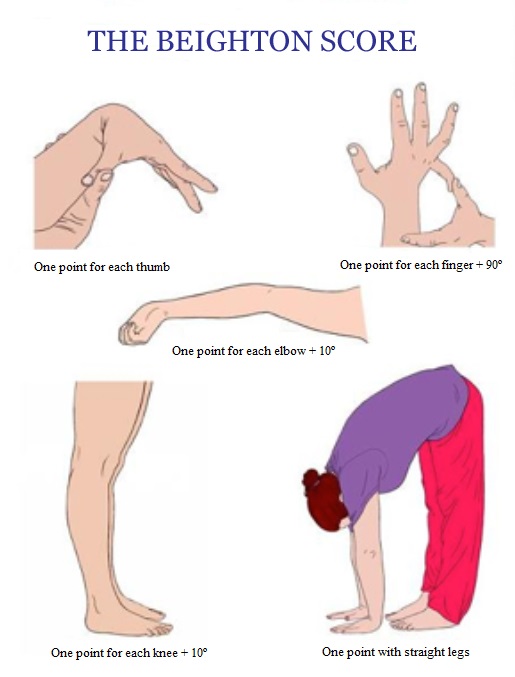
Beighton Score for Hypermobility Moving Naturally with
Joint hypermobility syndrome or double jointedness means that a person's joints bend more than usual. In some people, this can cause joint pain and injury. Jovo Jovanovic/Stocksy. Many different.

Practicing Yoga with Joint Hypermobility Syndrome/EDS The Hypermobile
The hypermobility syndrome(HMS) was first described in 1967 by Kirk et al as the occurrence of musculoskeletal symptoms in hypermobile healthy persons.[1] Meanwhile, other names are given to HMS, such as joint hypermobility syndrome and benign hypermobility joint syndrome. HMS is a dominant inherited connective tissue disorder described as "generalized articular hypermobility, with.
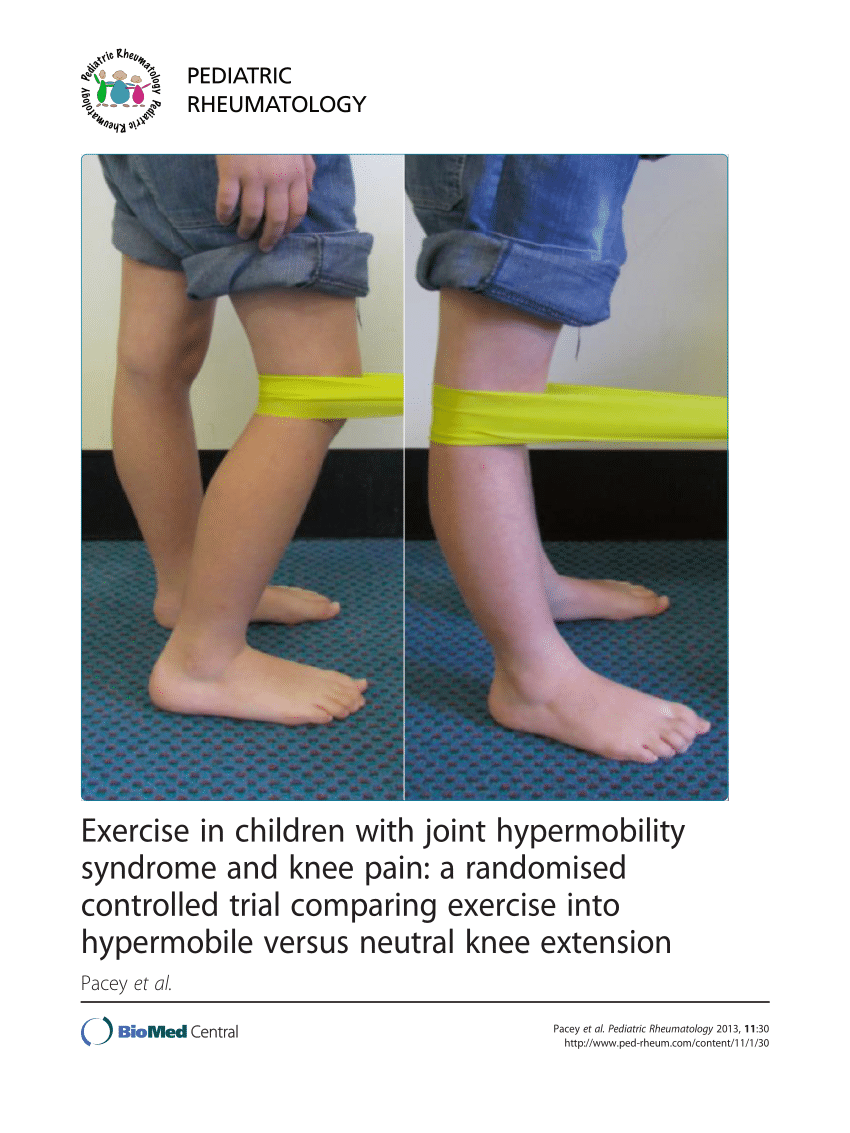
(PDF) Exercise in children with joint hypermobility syndrome and knee
Joint Hypermobility Syndrome (JHS) was first described in 1967 by Kirk and colleagues as a condition where joint laxity is associated with various musculoskeletal complaints.[1] JHS encompasses various disorders such as Benign Joint Hypermobility Syndrome (BJHS), Ehler-Danlos Syndrome (EDS), Marfan Syndrome and Osteogenesis Imperfecta.[2] All of these disorders are classified as.

Stabilise Hypermobile Shoulders Hypermobility & EDS Exercises with
For example, when weightlifting, you might feel as though your arms can come out of their sockets. (This is because those with hypermobility have joints that are typically looser than people without this condition.) Joint and muscle pain in the late afternoon or evening. Pain after exercise. Chronic pain in the calves, thighs, knees, and elbows.

The Best & Worst Activities for Hypermobile Joints
Exercise can also have condition specific benefits: Improve proprioception (the ability to sense the position of a joint) and balance. Improve muscle strength. Stabilise hypermobile joints. Maximise bone density, preventing or slowing the progression of osteoporosis. Reduce chronic pain. Enhance wellbeing.
Daily Exercises To Help Hypermobility Living with Hypermobility
Whereas a 9 would indicate Joint Hypermobility Syndrome (JHS). This is a more severe condition. Joint hypermobility syndrome.. As such, a certain degree of general fitness, activity levels, and exercise are vital for hypermobile individuals in guarding against the risk of injury. Maintaining a healthy weight is also crucial in avoiding pain.

Exercise for Hypermobile Hips and Knees Hypermobility & EDS Exercises
Introduction Rationale. Joint hypermobility syndrome (JHS) has been defined as a "heritable disorder of the connective tissues characterised by hypermobility, often affecting multiple joints, and musculoskeletal pains in the absence of systemic inflammatory joint disease such as rheumatoid arthritis" [1].Variation in diagnostic criteria makes interpretation of published literature.